Benchmark
All configuration files are located in the benchmark folder.
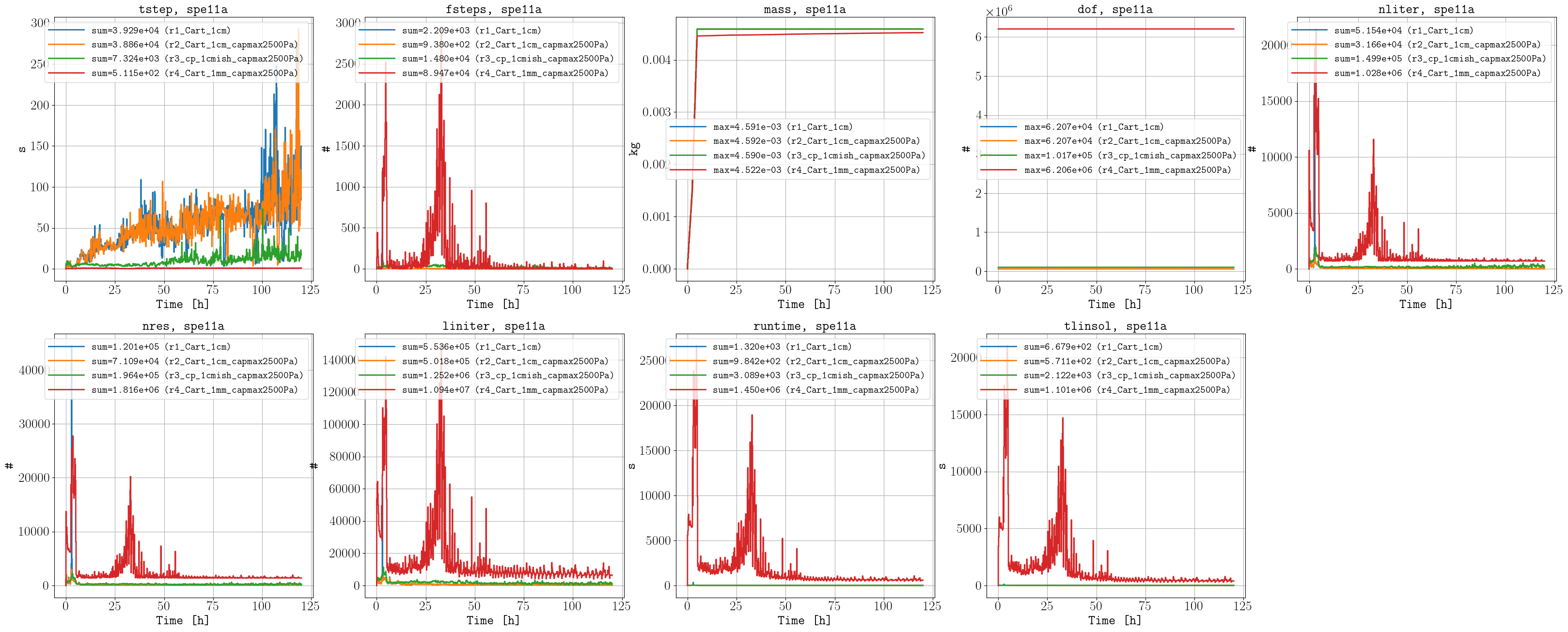
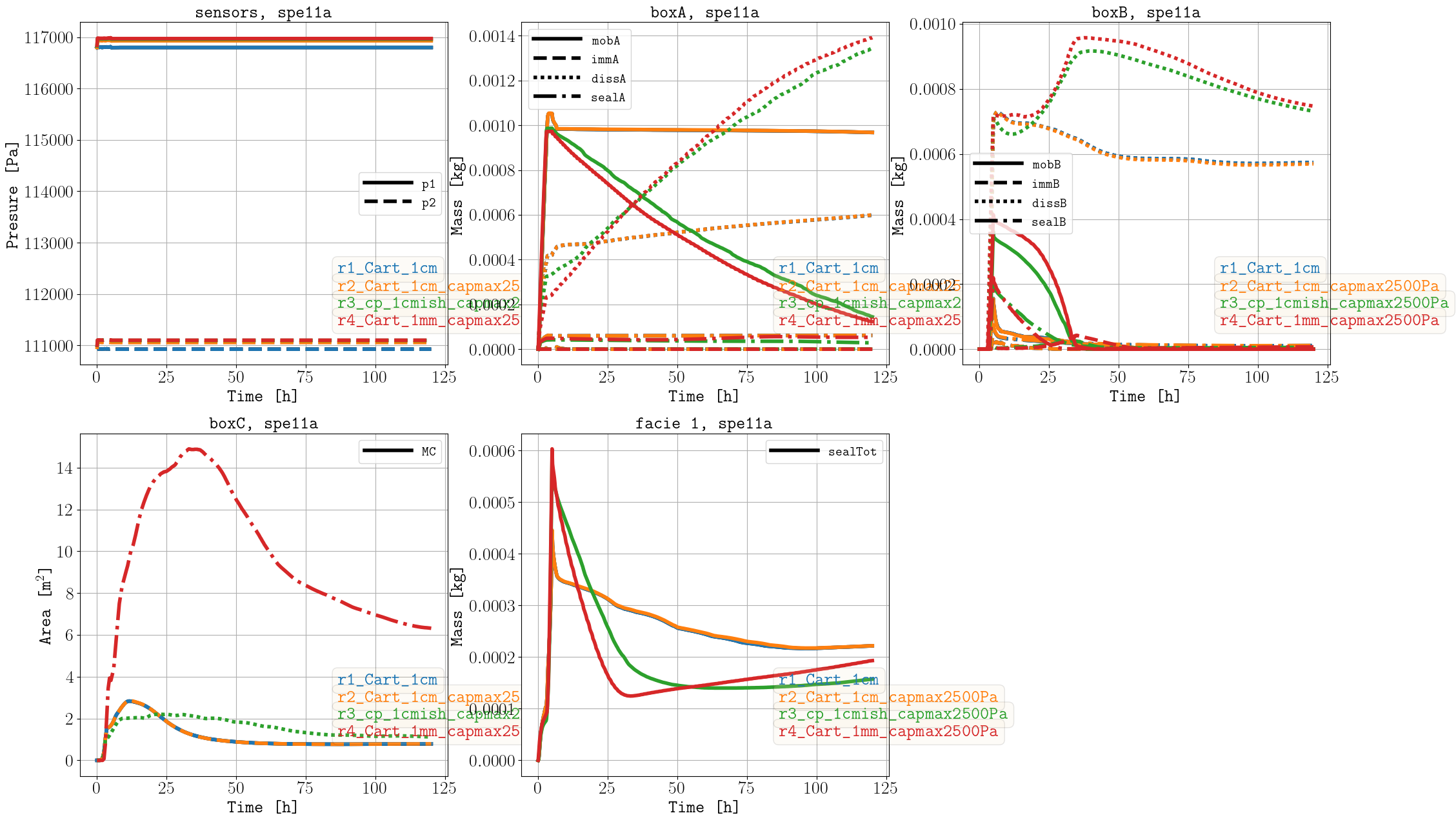
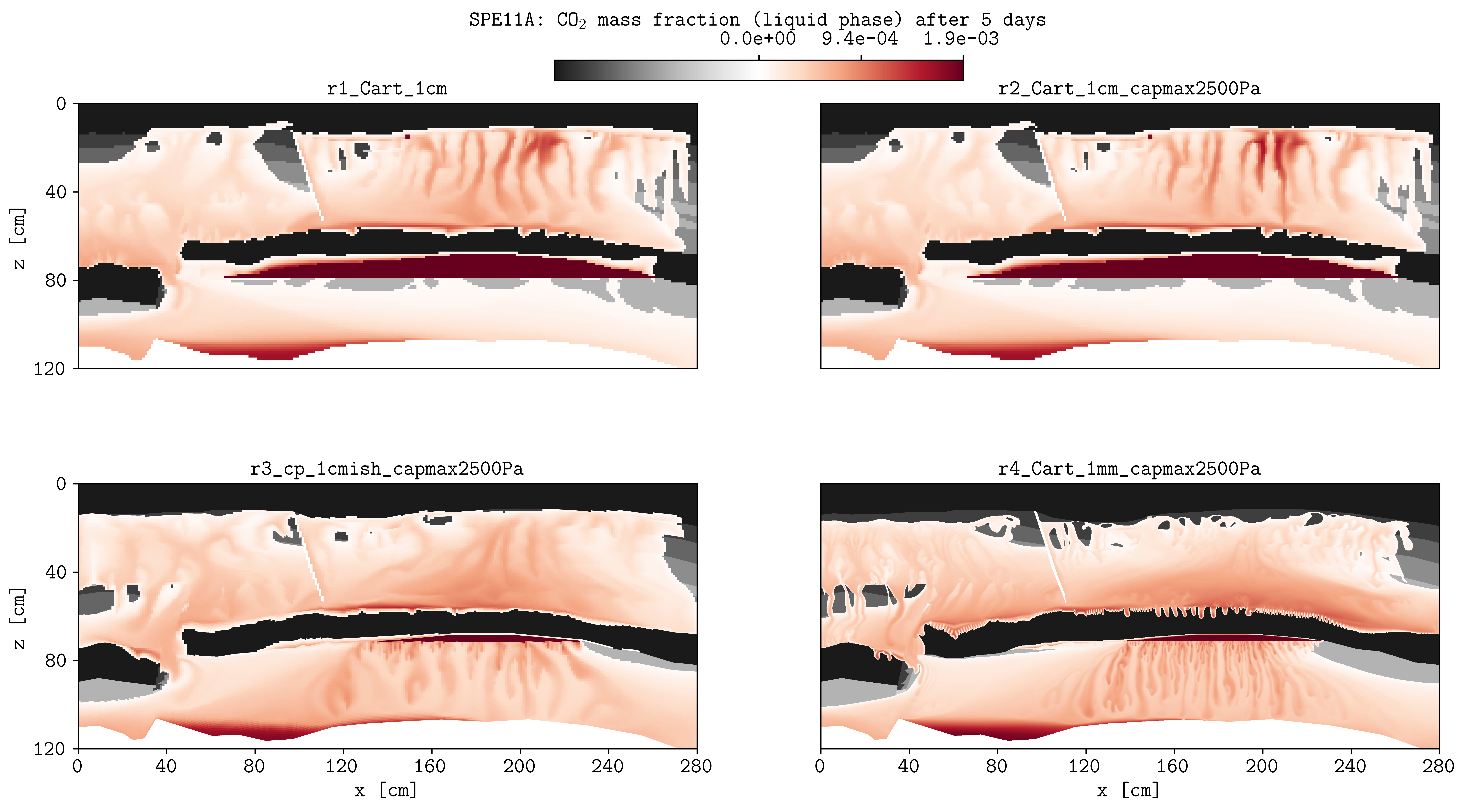
SPE11A
- r1_Cart_1cm
Uniform grid of 1 cm size
- r2_Cart_1cm_capmax2500Pa
Uniform grid of 1 cm size (maximum capillary pressure of 2500 Pa instead of 95000 Pa following the remarks in the benchmark description)
- r3_cp_1cmish_capmax2500Pa
Corner-point grid of ca. 1 cm size (maximum capillary pressure of 2500 Pa instead of 95000 Pa following the remarks in the benchmark description)
- r4_Cart_1mm_capmax2500Pa
Uniform grid of 1 mm size (maximum capillary pressure of 2500 Pa instead of 95000 Pa following the remarks in the benchmark description)
- r5_Cart_1mm_capmax2500Pa_strictol
Uniform grid of 1 mm size with stricter tolerances (maximum capillary pressure of 2500 Pa instead of 95000 Pa following the remarks in the benchmark description)
To run the cases in the terminal:
pyopmspe11 -i r1_Cart_1cm.toml -o r1_Cart_1cm -m all -g all -t 1 -r 280,1,120 -w 0.16666666666666666
pyopmspe11 -i r2_Cart_1cm_capmax2500Pa.toml -o r2_Cart_1cm_capmax2500Pa -m all -g all -t 1 -r 280,1,120 -w 0.16666666666666666
pyopmspe11 -i r3_cp_1cmish_capmax2500Pa.toml -o r3_cp_1cmish_capmax2500Pa -m all -g all -t 1 -r 280,1,120 -w 0.16666666666666666
pyopmspe11 -i r4_Cart_1mm_capmax2500Pa.toml -o r4_Cart_1mm_capmax2500Pa -m all -g all -t 1 -r 280,1,120 -w 0.16666666666666666
pyopmspe11 -i r5_Cart_1mm_capmax2500Pa_strictol.toml -o r5_Cart_1mm_capmax2500Pa_strictol -m all -g all -t 1 -r 280,1,120 -w 0.16666666666666666
As mentioned in the CSP description, using the maximum value of 2500 Pa instead of 95000 Pa does not significantly impact the results (comparing r1 and r2), and this choice also reduces the simulation time. In addition, the corner-point grid results (r3) compare very well to the fine-scale simulations (r4). Unfortunately, the fine-scale simulation with stricer tolerances (r5) finished after the benchmark submission deadline; nevertheless, we include it here for comparison to the other cases. While the case with stricter tolerances (r5) improves the mass issue compared to the previous case (r4), the simulation time increased, which highlights the trade-off between simulation time and accuracy (i.e., which is relevant for optimization studies which require to run many simulations).
Performance data
Sparse data
Spatial maps
SPE11B
- r1_Cart_10m
Uniform grid of 10 m size (1 m dx size on left and right boundaries)
- r2_cp_10mish
Corner-point grid of ca. 10 m size (1 m dx size on left and right boundaries)
- r3_cp_10mish_convective
Corner-point grid of ca. 10 m size (1 m dx size on left and right boundaries) using a subgrid model for convective mixing for facies 2 and 5.
- r4_Cart_1m
Uniform grid of 1 m size
To run the cases in the terminal:
pyopmspe11 -i r1_Cart_10m.toml -o r1_Cart_10m -m all -g all -r 840,1,120 -t 5 -w 0.1
pyopmspe11 -i r2_cp_10mish.toml -o r2_cp_10mish -m all -g all -r 840,1,120 -t 5 -w 0.1
pyopmspe11 -i r3_cp_10mish_convective.toml -o r3_cp_10mish_convective -m all -g all -r 840,1,120 -t 5 -w 0.1
pyopmspe11 -i r4_Cart_1m.toml -o r4_Cart_1m -m all -g all -r 840,1,120 -t 5 -w 0.1
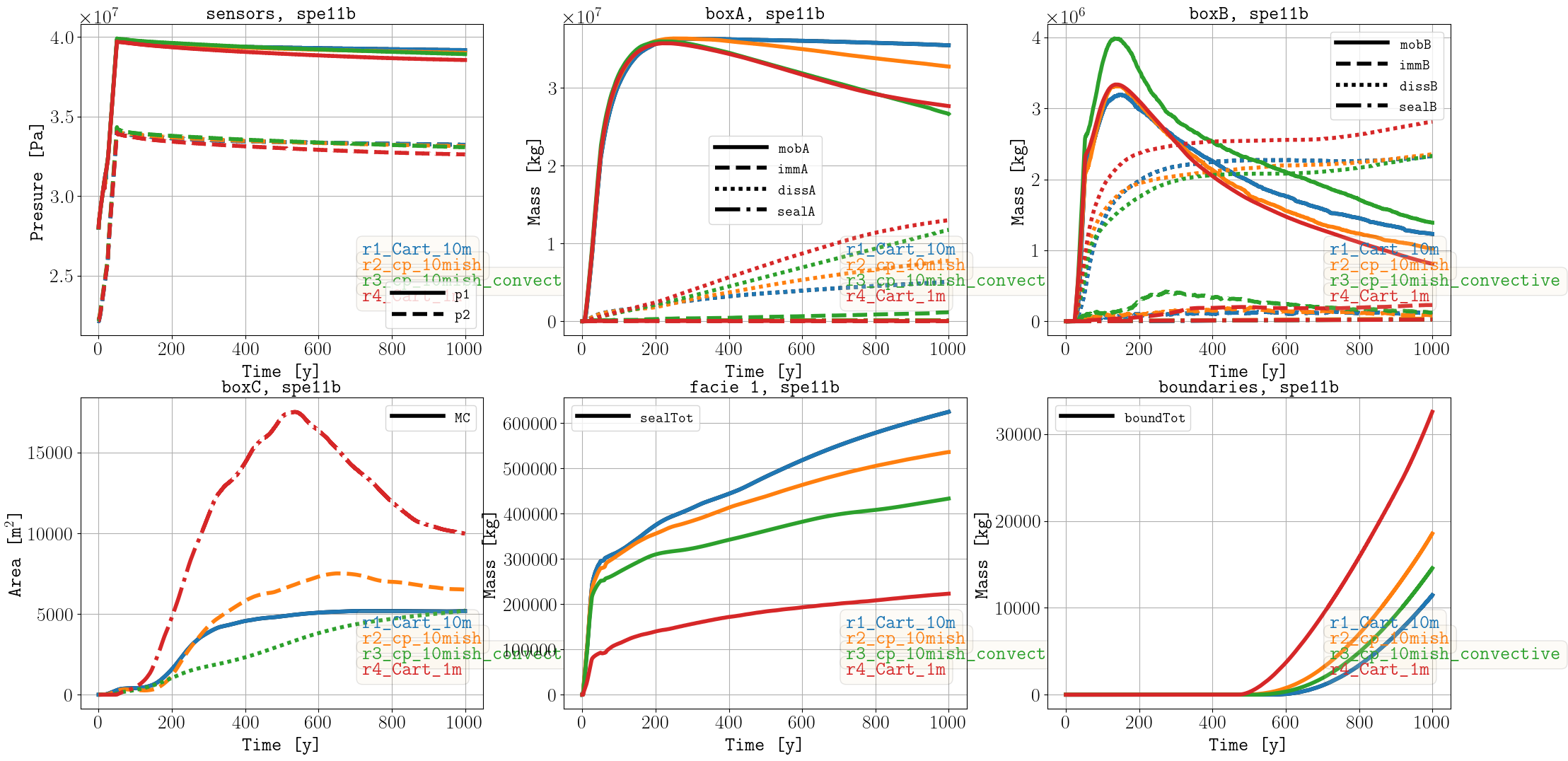
For the box A quantities, the convective model results (r3) compare very well to the fine-scale simulations (r4), which runs ca. 500 times faster. Details on the convective model can be found in Mykkeltvedt et al. (2025). For the implementation in OPM Flow of this model, it is work in progress to handle better the zones in the geological model where dissolve CO2 accumulates.
Performance data
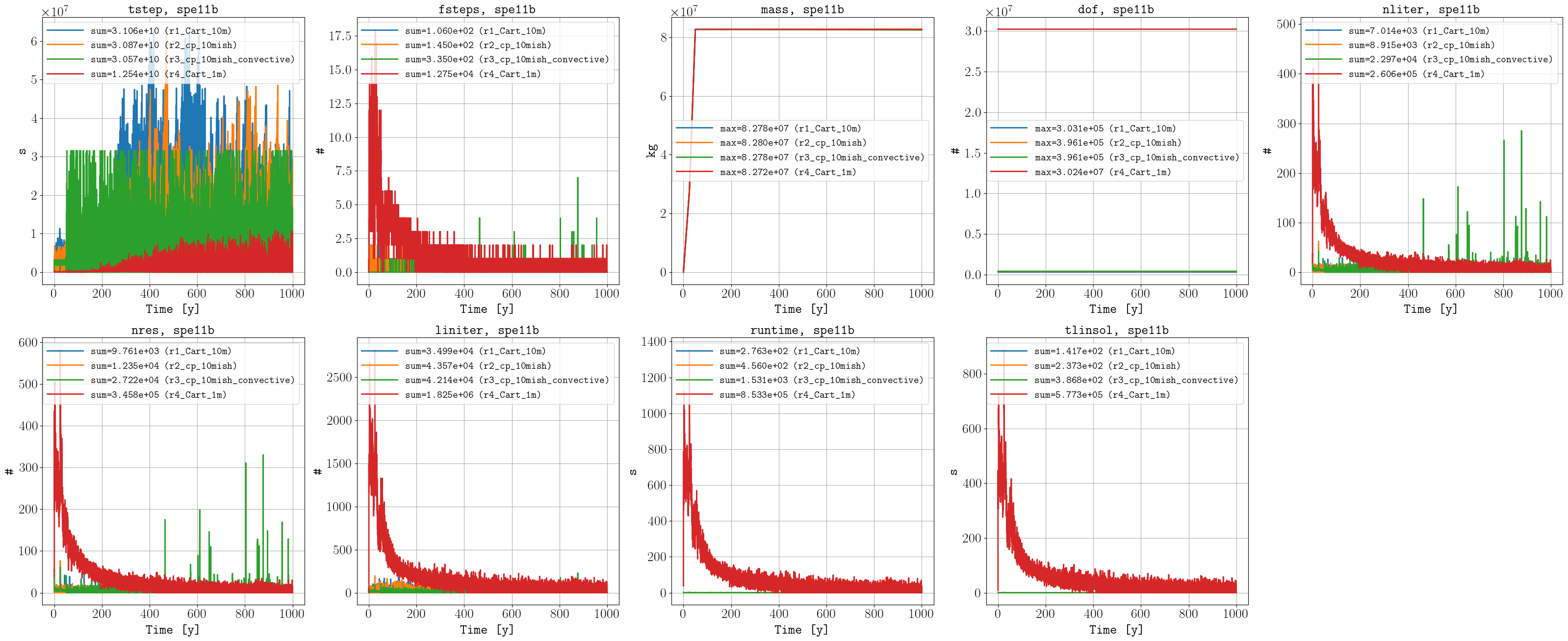
Sparse data
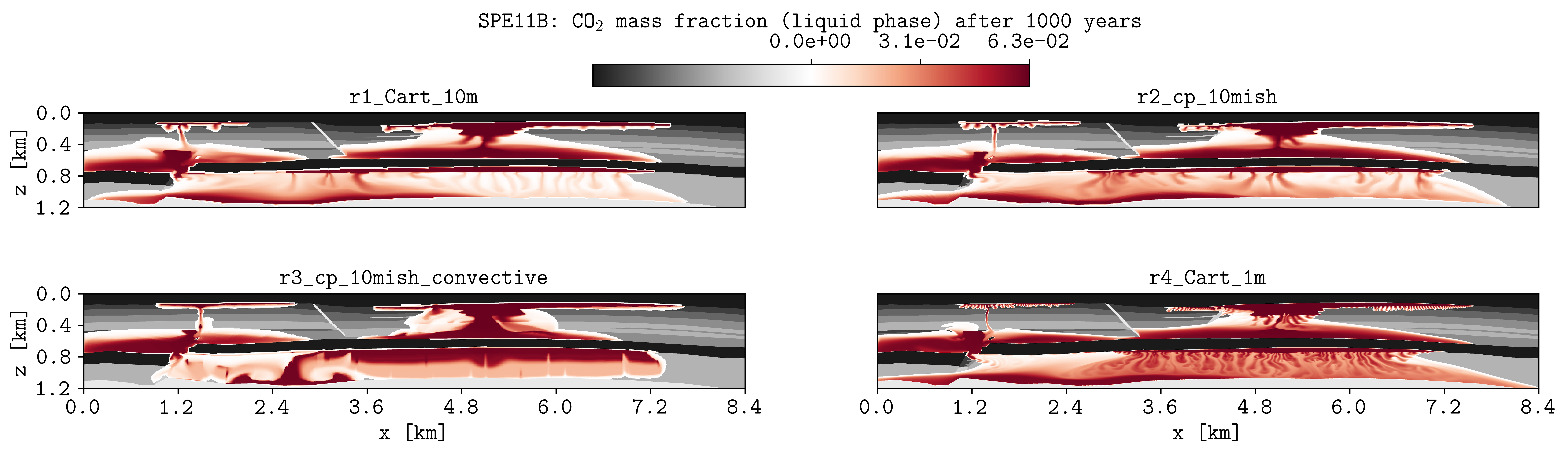
Spatial maps
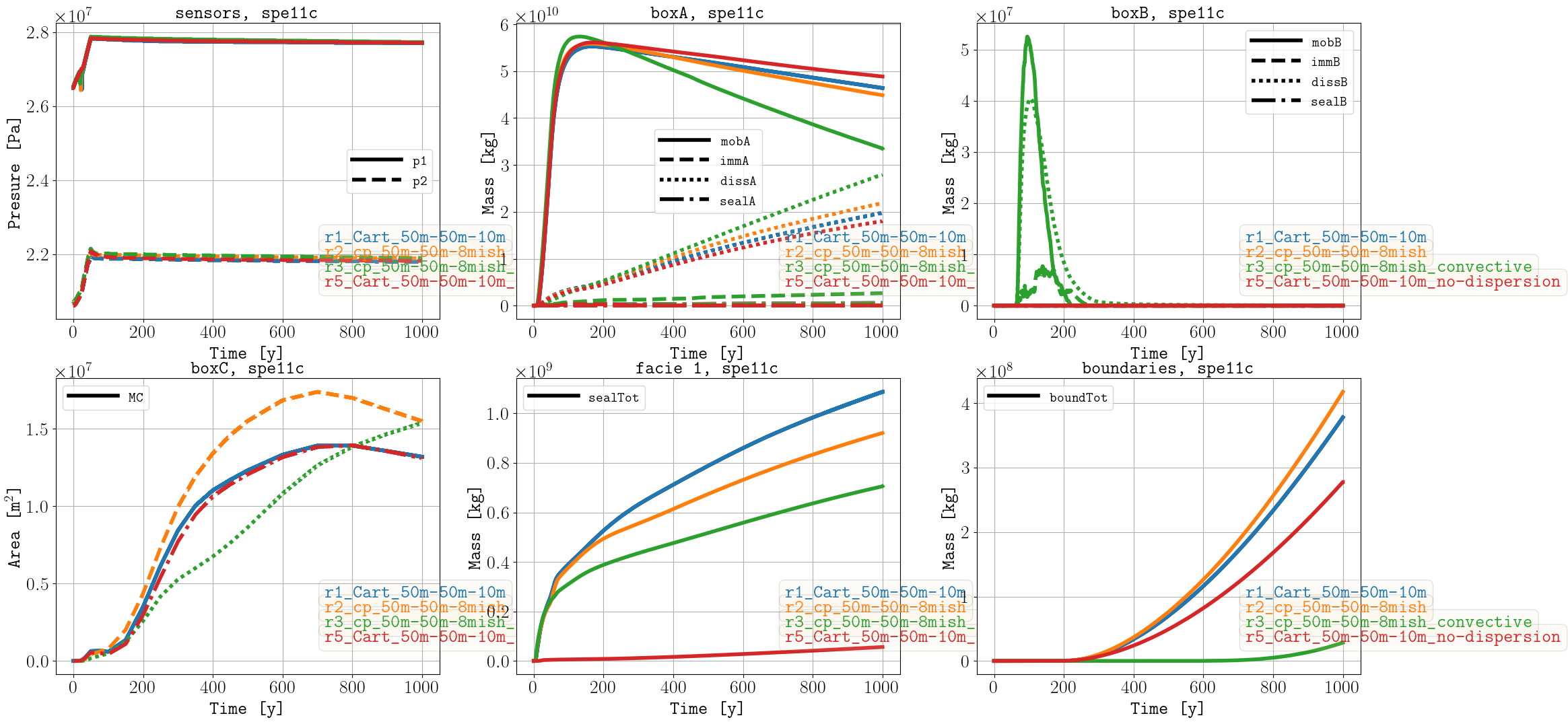
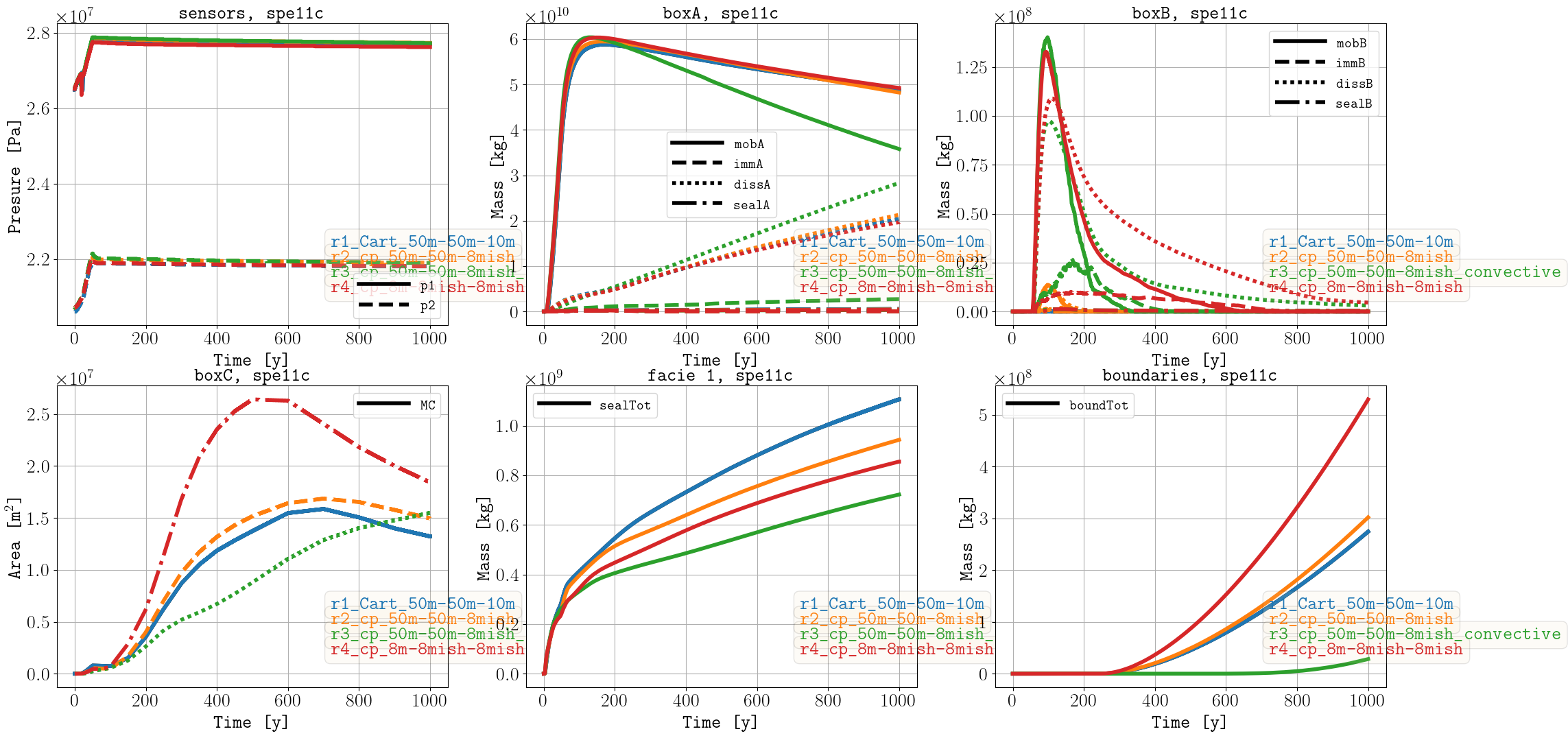
SPE11C
- r1_Cart_50m-50m-10m
Grid of [50, 50, 10] m size (1 m dx size on left and right boundaries and 1 m dy size on back and front boundaries)
- r2_cp_50m-50m-8mish
Corner-point grid of [50, 50, mean ca. 8] m size (1 m dx size on left and right boundaries and 1 m dy size on back and front boundaries)
- r3_cp_50m-50m-8mish_convective
Corner-point grid of [50, 50, mean ca. 8] m size (1 m dx size on left and right boundaries and 1 m dy size on back and front boundaries) using the convective model for facies 2 and 5.
- r4_cp_8m-8mish-8mish
Corner-point grid of [8, mean ca. 8, mean ca. 8] m size (1 m dx size on left and right boundaries and 1 m dy size on back and front boundaries)
To run the cases in the terminal:
pyopmspe11 -i r1_Cart_50m-50m-10m.toml -o r1_Cart_50m-50m-10m -m all -g all -r 168,100,120 -t 0,5,10,15,20,25,30,35,40,45,50,75,100,150,200,250,300,350,400,450,500,600,700,800,900,1000 -w 0.1
pyopmspe11 -i r2_cp_50m-50m-8mish.toml -o r2_cp_50m-50m-8mish -m all -g all -r 168,100,120 -t 0,5,10,15,20,25,30,35,40,45,50,75,100,150,200,250,300,350,400,450,500,600,700,800,900,1000 -w 0.1
pyopmspe11 -i r3_cp_50m-50m-8mish_convective.toml -o r3_cp_50m-50m-8mish_convective -m all -g all -r 168,100,120 -t 0,5,10,15,20,25,30,35,40,45,50,75,100,150,200,250,300,350,400,450,500,600,700,800,900,1000 -w 0.1
pyopmspe11 -i r4_cp_8m-8mish-8mish.toml -o r4_cp_8m-8mish-8mish -m all -g all -r 168,100,120 -t 0,5,10,15,20,25,30,35,40,45,50,75,100,150,200,250,300,350,400,450,500,600,700,800,900,1000 -w 0.1
To run the case with more than 100 million cells (r4), it required improvements in the OPM Flow simulator (e.g., METIS support), as well as in the pyopmspe11 pre- and postprocessing functionality (and of course a big computer, the NORCE HPC cluster). See this gif for visualization in ParaView of the CO2 molar fraction (liquid phase) over time.
Performance data
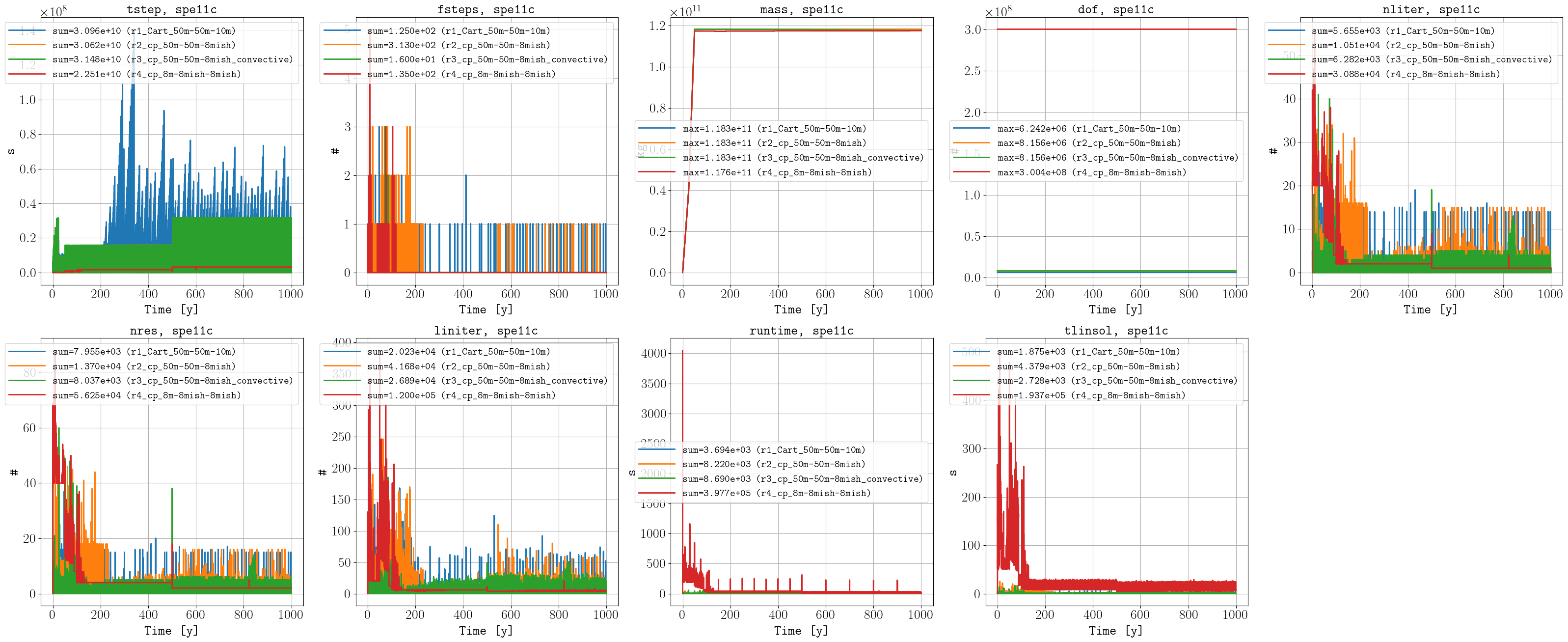
Sparse data
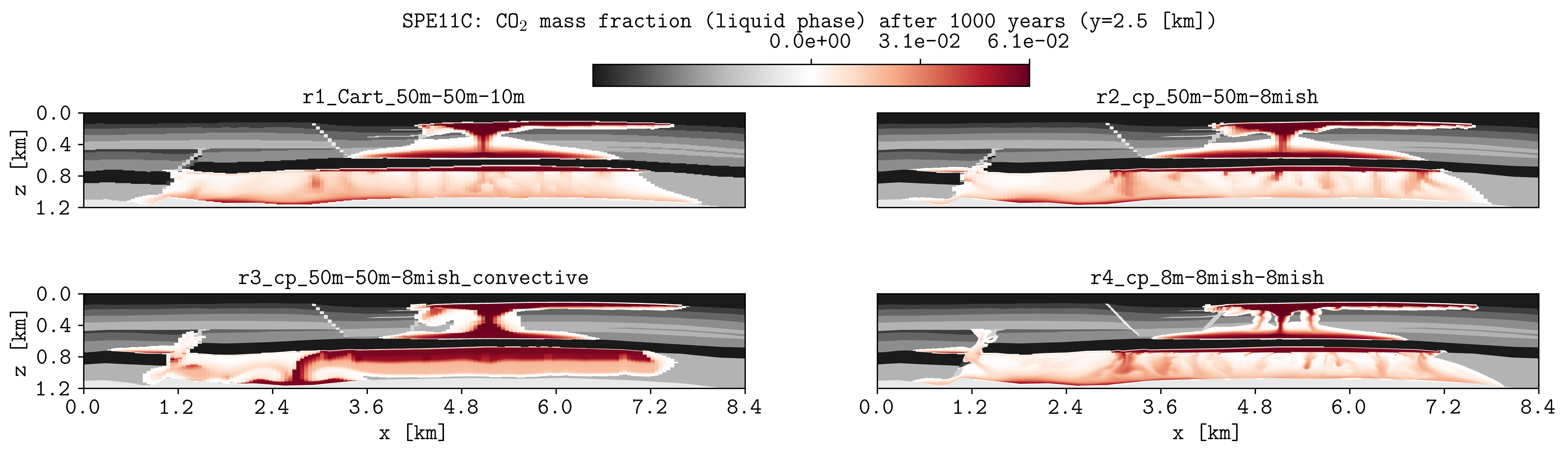
Spatial maps
Note
To show the high resolution results, all spatial maps (spe11a, spe11b, and spe11c) corresponds to the actual simulation grid (not the benchmark reporting grid), and can be generated by typing in the terminal:
plopm -v xco2l -i 'r1_Cart_1cm/flow/R1_CART_1CM r2_Cart_1cm_capmax2500Pa/flow/R2_CART_1CM_CAPMAX2500PA r3_cp_1cmish_capmax2500Pa/flow/R3_CP_1CMISH_CAPMAX2500PA r4_Cart_1mm_capmax2500Pa/flow/R4_CART_1MM_CAPMAX2500PA' -dpi 300 -c cet_diverging_protanopic_deuteranopic_bwy_60_95_c32 -cnum 3 -xlnum 8 -clabel 'SPE11A: CO$_2$ mass fraction (liquid phase) after 1 day' -d 16,6.5 -t "r1 Cart 1cm r2 Cart 1cm capmax 2500 Pa r3 cp 1cmish capmax 2500 Pa r4 Cart 1mm capmax 2500 Pa" -yunits cm -xunits cm -yformat .0f -xformat .0f -r 29 -save massfracta -cformat .2e -mask satnum -maskthr 7e-5 -suptitle 0 -subfigs 2,2 -cbsfax 0.35,0.97,0.3,0.02 -delax 1
plopm -v xco2l -i "r1_Cart_10m/flow/R1_CART_10M r2_cp_10mish/flow/R2_CP_10MISH r3_cp_10mish_convective/flow/R3_CP_10MISH_CONVECTIVE r4_Cart_1m/flow/R4_CART_1M" -dpi 300 -c cet_diverging_protanopic_deuteranopic_bwy_60_95_c32 -cnum 3 -xlnum 8 -clabel 'SPE11B: CO$_2$ mass fraction (liquid phase) after 500 years' -d 16,3 -t "r1 Cart 10m r2 cp 10mish r3 cp 10mish convective r4 Cart 1m" -yunits km -xunits km -yformat .1f -xformat .1f -r 98 -save massfractb -cformat .2e -mask satnum -maskthr 5e-3 -suptitle 0 -subfigs 2,2 -cbsfax 0.35,0.97,0.3,0.02 -delax 1
plopm -v xco2l -i "r1_Cart_50m-50m-10m/flow/R1_CART_50M-50M-10M r2_cp_50m-50m-8mish/flow/R2_CP_50M-50M-8MISH r3_cp_50m-50m-8mish_convective/flow/R3_CP_50M-50M-8MISH_CONVECTIVE r4_cp_8m-8mish-8mish/flow/R4_CP_8M-8MISH-8MISH" -dpi 300 -c cet_diverging_protanopic_deuteranopic_bwy_60_95_c32 -cnum 3 -xlnum 8 -clabel 'SPE11C: CO$_2$ mass fraction (liquid phase) after 1000 years (y=2.5 [km])' -d 16,3 -t "r1 Cart [50m,50m,10m] r2 cp [50m,50m,8mish] r3 cp [50m,50m,8mish] convective r4 cp [8m,8mish,8mish]" -yunits km -xunits km -yformat .1f -xformat .1f -r 27 -save massfractc -cformat .2e -mask satnum -maskthr 1e-4 -suptitle 0 -subfigs 2,2 -cbsfax 0.30,0.97,0.4,0.02 -delax 1 -s ',51, ,51, ,51, ,304,'
Tip
You can install plopm by executing in the terminal:
pip install git+https://github.com/cssr-tools/plopm.git
Well 1 correction
In the submitted results for SPE11C, the Well 1 was located ca. 100 m above the 300 m depth specified in the benchmark. The results belowed show the sparse data with the correct location of the well (results without dispersion on the reporting grid (r5, generated by setting DISP to 0 in r1) are showed instead of the large model (r4)).