Overview
User Interface
ResInsight has two main windows, one for 3D related visualizations and one for 2D graphs and plots.
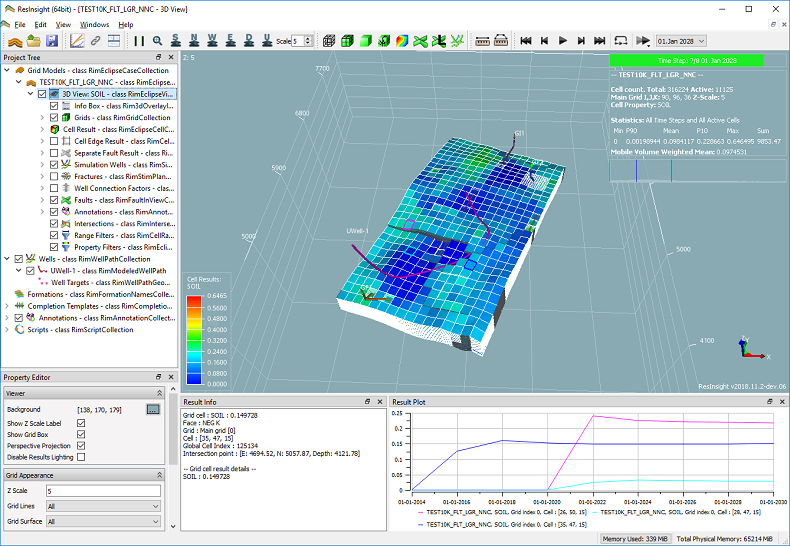
3D Main Window
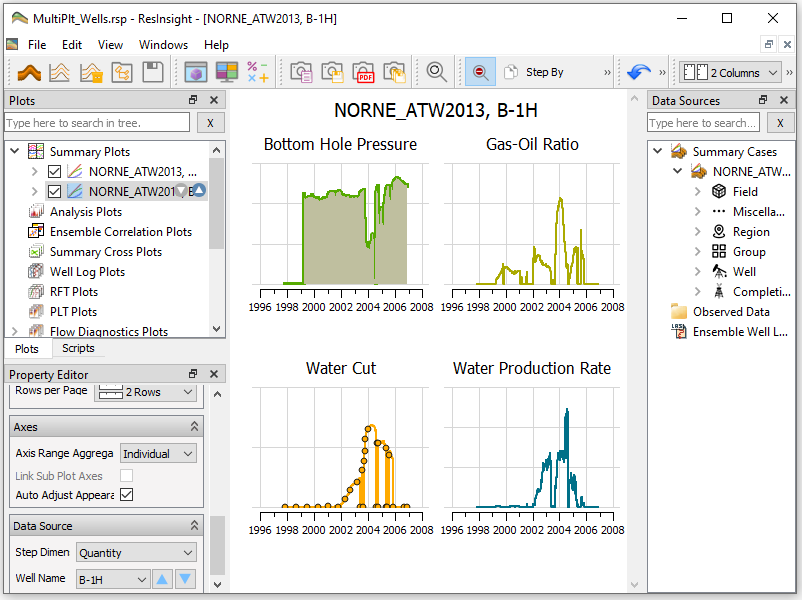
Plot Main Window
Switching Between the Two Main Windows
The two main windows has a toolbar button each, that directly opens and raises the other window.


Each of the windows can also be closed freely, but if both are closed, ResInsight exits.
Docking Windows
Each of the main windows has a central area and several docking windows surrounding it. The different docking windows can be managed from the Windows menu or directly using the local menu bar of the docking window.
- Project Tree – contains all application objects in a tree structure.
- Property Editor – displays all properties for the selected object in the Project Tree
- Process Monitor – displays output from Octave when executing Octave scripts
- Result Info – displays info for the selected object in the 3D scene
- Result Plot – displays curves based on result values for the selected cells in the 3D scene
- Messages – displays occasional info and warnings related to operations executed.
Result Info and Result Plot is described in detail in Result Inspection
Note
Use several Project Trees and Property Editors: If you want to pin the property editor for a certain object, you can add a new Project Tree and Property Editor by using the command Windows->New Project and Property View.
Toolbars
A selected subset of actions are presented as controls in the toolbar. The different sections in the toolbar can be dragged and positioned anywhere as small floating toolbars. Management of the toolbar is done by right-clicking on the toolbar and then manipulating the displayed menu.
Managing 3D Views and Plot Windows
In the main area of the application, several 3D views or plot windows can be open at the same time. One of them will be active and the active view can be either maximized to use the whole main area, or restored so that you can see the open windows.
Standard window management for applying minimized, normal and maximized state is available in the upper right corner.
Commands to arrange the windows in the standard ways are available from the Windows menu
- Tile Windows – distribute all open view windows to fill available view widget space
- The order of the tiled windows are determined by the window positions and the type of view at the time of running the tile command. The leftmost window are tiled first, then the next leftmost and so on. Master views are tiled before slave views.
- Cascade Windows – organize all open view windows slightly offset on top of each other
- Close All Windows – close all open view windows
Editing 3D Views and Plot Windows Content
Most of the settings and features of ResInsight is accessible through the Project Tree and the Property Editor. Selecting an item in the Project Tree activates the corresponding Window, and shows the item properties in the Property Editor available for editing.
Toggling a checkbox next to an item in the Project Tree will toggle visibility in the window. Toggling a checkbox for a collection of items will affect the visibility for all items in the collection
 .
Right-click menu commands are also available to do special operations on a selected set of items.
.
Right-click menu commands are also available to do special operations on a selected set of items.
ResInsight stores all views and settings in a Project File to easily continue the work in a subsequent session.
Model Navigation describes how to interact and manipulate the 3D model.
Cases and Their Types
A Case in ResInsight means a Grid model with a particular set of results or property data. There are three different types of reservoir simulation cases and one type of Geomechanical cases.
Eclipse Cases
The following Eclipse cases can be imported into ResInsight via the File->Import->Eclipse Cases menu, see Import Eclipse Cases:
Result Case

This is a Case based on the results of a reservoir simulation, read from a grid file together with static and restart data. Multiple Cases can be selected and read from a folder.
Input Case

This Case type is based on a *.GRDECL file, or a part of a reservoir simulation input file. This Case type supports loading single ASCII files defining reservoir simulation properties, and also to export modified property sets to ASCII files.
Each of the reservoir simulation properties are listed as separate entities in the Project Tree, and can be renamed and exported.
See Grid Import and Property Export
Statistics Case

This is a Case type that belongs to a Grid Case Group and makes statistical calculations based on the source cases in the Grid Case Group. See Grid Case Groups and Statistics .
Summary Case

This is the case type listed in the Plot Main Window, and represents an *.SMSPEC file. These Cases are available for Summary Plotting. See Summary Plots .
Geomechanical cases
There are only one type of geomechanical
 cases, namely the ABAQUS-odb case type.
When ResInsight is compiled with ABAQUS-odb support,
cases, namely the ABAQUS-odb case type.
When ResInsight is compiled with ABAQUS-odb support, *.odb files can be imported by selecting the menu item:
File->Import->Geo Mechanical Cases->
 Import Geo Mechanical Model.
Import Geo Mechanical Model.
The geomechanical cases are sorted into its own folder in the project tree named Geomechanical Models
 as opposed to the Grid Models folder where the reservoir simulation cases and Grid Case Groups resides.
as opposed to the Grid Models folder where the reservoir simulation cases and Grid Case Groups resides.
See Build Instructions on how to compile ResInsight with odb-support.
Grid Case Groups
A Grid Case Group
 is a group of Result Cases with identical grids, but generally different active cells, initial values and results. These cases are called Source Cases. The purpose of a Grid Case group is to make it easy to calculate statistics across the source cases both for static and dynamic reservoir simulation properties. See Grid Case Groups and Statistics .
is a group of Result Cases with identical grids, but generally different active cells, initial values and results. These cases are called Source Cases. The purpose of a Grid Case group is to make it easy to calculate statistics across the source cases both for static and dynamic reservoir simulation properties. See Grid Case Groups and Statistics .